Configuration
How to Configure CacheNinja
The plugin configuration settings are presented as straight-forward options.
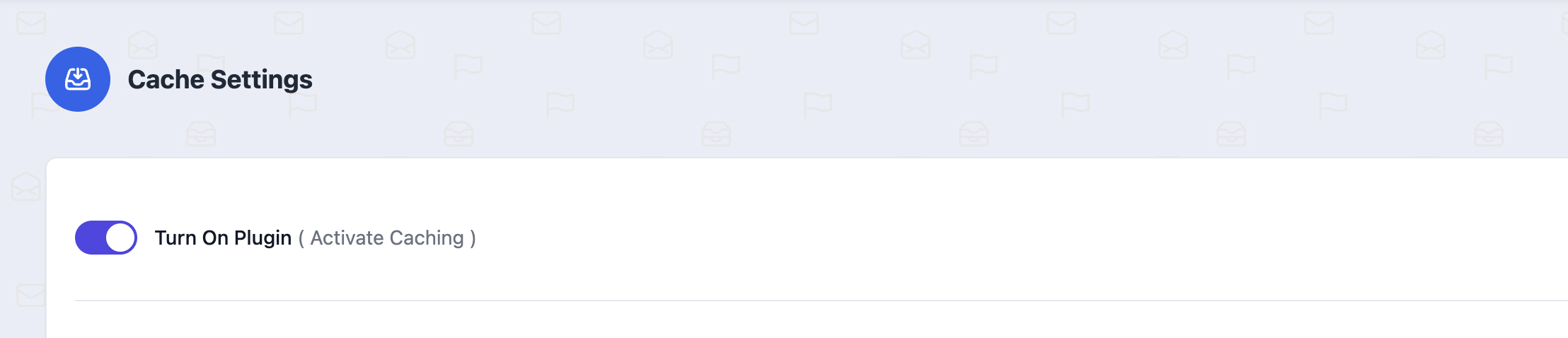
1. Activate or Deactivated
CacheNinja presents a primary toggle switch that allows you to turn the plugin on or off (without the need to deactivate the plugin from within the WordPress Plugins section.
2. CSS Options
The following CSS options are provided in detail below:
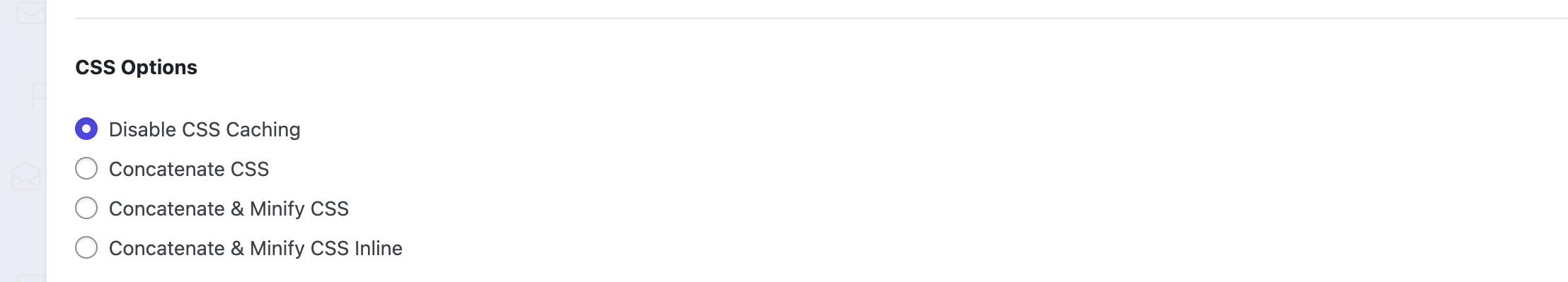
Disable CSS Caching
This setting prevents the browser or server from storing and reusing CSS files across visits.
Concatenate CSS
Combines multiple CSS files into a single file. This option reduces the number of HTTP requests made by the browser, which can speed up page load times—especially on older HTTP/1.1 servers.
Concatenate & Minify CSS
Combines multiple CSS files into one file and removes unnecessary characters like spaces, line breaks, and comments to reduce file size. Use Case: Great for production environments to improve performance by reducing load times and bandwidth usage.
Important Note
Can sometimes break styles if plugins/themes use improperly scoped or conflicting CSS.
Concatenate & Minify CSS Inline
Minifies and combines the CSS, then embeds the result directly into the HTML head as inline code (instead of linking to an external CSS file). This can improve initial page load speed and Core Web Vitals (like First Contentful Paint) for small sites or critical-path CSS.
3. Javascript Options
CacheNinja's Javascript options are provided in detail below:

Disable JS Caching
This setting prevents JavaScript files from being cached by the browser or a caching layer. This option can be useful during development or debugging (to ensure the latest JavaScript changes are always loaded). When enabled - slower page load times on repeat visits occur, since JS files must be re-downloaded every time.
Concatenate JS
This option combines multiple JavaScript files into one or a few larger files. The result reduces the number of HTTP requests, which improves performance—especially on HTTP/1.1 servers. Downside: Errors in one script can affect others in the same bundle.
Concatenate & Minify JS
This combines multiple JavaScript files into one and removes unnecessary characters like whitespace, comments, and line breaks - to reduce file size. This improves page load speed by reducing both request count and file size.
Important Note
This setting can sometimes cause JavaScript conflicts or break functionality if there are dependencies that rely on specific loading orders (especially with inline scripts or jQuery). Test your implementation thorougly.
4. Defer JS Settings
These options either adds the defer attribute to script tags, telling the browser to: Download JS in parallel while parsing the HTML or not.
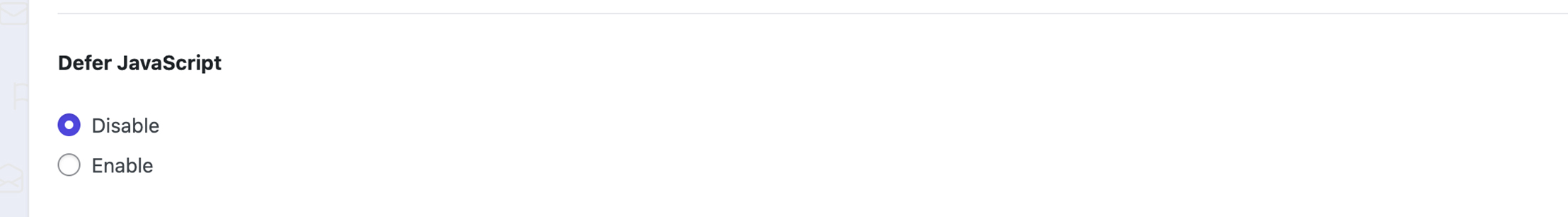
Disable (Defer JavaScript)
JavaScript files will load normally, in the order they appear in the page source, often before the page content is fully rendered. Use Case: Use this if you're experiencing broken scripts, layout shifts, or issues with time-sensitive JavaScript (e.g., above-the-fold animations).
Enable (Defer JavaScript)
Inserts the defer attribute into script tags, instructing the browser to download JavaScript during page parsing but delay execution until after the HTML is fully loaded. This setting improves performance and Core Web Vitals (especially First Contentful Paint) by letting the browser prioritize content over scripts. This is ideal for most modern sites.
5. Browser Caching Options
Learn about the Browser Cache Options the plugin provides below:
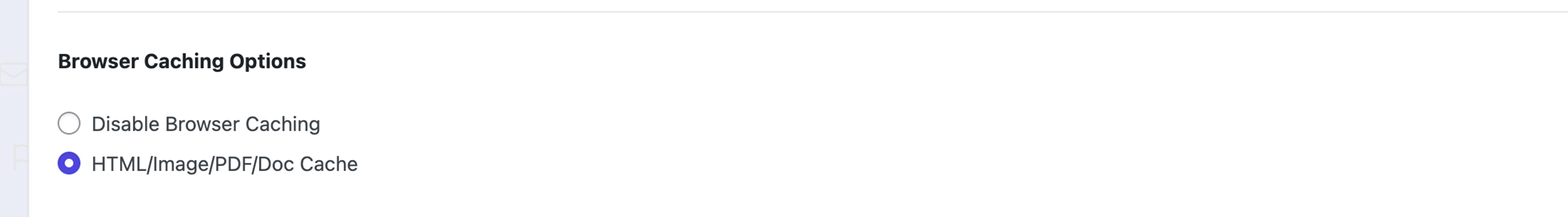
Disable Browser Caching
This option turns off browser caching headers entirely, meaning browsers will not store static files (like images, CSS, or JavaScript) locally for reuse on future visits. Every page load will re-download these assets from the server. This setting is only recommended for debugging or during active development - when you want to make sure users always get the most recent file version. This option is not recommended for live or production sites.
HTML/Image/PDF/Doc Cache
This enables browser caching for common static file types like:
- .html, .htm (HTML content)
- .jpg, .png, .svg, .gif (Images)
- .pdf, .doc, .docx (Documents)
When this option is enabled, your server sends caching headers that tell browsers to store these files locally for a set period so they don’t need to be re-downloaded every time a user visits your site. This option is great for improving page speed, especially for returning visitors. This is ideal for sites with media-heavy content or downloadable files: reduces page load time on repeat visits, saves bandwidth and reduces server load and improves Core Web Vitals and overall user experience.
6. Grouping Option Settings
Read below for a breakdown of each of the two grouping option:
Site-wide ( Generates one CSS & JS file )
This option creates a single, shared CSS and JS file that is used across your entire website — regardless of which page is loaded. This is ideal for websites with a consistent layout and design across all pages (e.g., blogs, landing pages, brochure sites). This can improves cache efficiency — once the user loads a CSS/JS file on one page, it’s cached for all others. Note: This setting can include unnecessary CSS or JS on some pages (code bloat), especially if different plugins or blocks are only used on specific pages. Potentially not ideal for highly custom/ modular sites which rely on highly specific JS files for many different components or WooCommerce sites.
Unique Page (Generates individual CSS & JS files for each page)
This option generates a separate CSS and JS file for each page based on only the assets that are actually used on that page. This is ideal for: complex or modular sites where each page uses distinct layouts, widgets, or plugin elements (e.g., WooCommerce product pages, custom landing pages, Elementor-heavy builds). This is option provides leaner, more efficient code per page and avoids loading unused styles/scripts. This setting also improves first-load speed and Total Blocking Time (TBT).
Speed Up Your Website Today
Drastically reduce your WordPress load times, generate increased conversions and avoid wasting revenue.
The WordPress® trademark is the intellectual property of the WordPress Foundation. Uses of the WordPress®, names in this website are for identification purposes only and do not imply an endorsement by WordPress Foundation. PluginBank is not endorsed or owned by, or affiliated with, the WordPress Foundation.